Sunday, 22 May 2011
4.7 - Energy efficiency
Out of 100% of energy only 10% makes it to the next trophic level (primary consumer)
And only 1% of that makes it to the secondary consumer
The loss of energy is because the organism needs to:
-Respire
-Grow
-Move
Another reason for the lost of energy is that, for example:cellulose, cannot be digested so the energy is lost through faeces.
4.6 - Transfer of substances and energy along the food chain
-Producer (grass) - Transfers light energy (from the sun) to chemical enegry
-Chemical energy = organic molecules
- This includes carbohydrates, protein and lipids (food)
-These molecules and up being food for the primary, secondary and tertiary consumers
-The energy consumed is used for:
-Growth
-Respiration
-Life processes
Bonds:
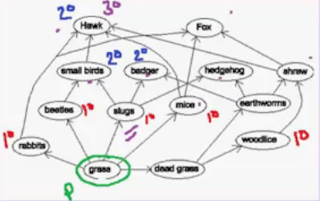
4.5b - Food Webs
1) The food web provides a better description of the ecosystem.
2) The food webs shows organisms feeding at different trophic levels
Consequences of (2):
1.Organisms can have multiple predators
2.It could be feeding on multiple pray.
3.This results in the food chain being linked
4.5a - Food Chain
This links together {{ Producer ----> Primary consumer ----> Secondary consumer ----> Tertiary consumer}}
-You cant show an organism being an omnivore
-You cant show organism feeding at more than 2 trophic levels
Food chains shows the flow of matter and energy
4.4- Trophic Levels
Trophic = feed
trophic levels = feeding levels
Primary consumer: Eats the producer (producer = changes light energy to chemical energy)
Secondary consumer: Eats the primary consumer (turns the energy to its own)
Tertiary consumer: Eats the secondary consumer (turns the energy to its own)
Tuesday, 10 May 2011
4.3 Quadrates samples
-Use quadrates to sample the population
The samples have to be: -Random
-Large
-Random number (for the grid, x & y coordinates)
-Count the number of daisies (species) in one of the squares
-That ='s 10% of the original area.
Monday, 9 May 2011
4.2 Quadrates
Quatrating:
1. Count the number of individuals in the population
2. Quadraring is used to sample an area and count the number of individuals in that area
3.This is repeated a number of times to gain an estimate of the population size
(quadrating is a method of sampling different locations to compare them)
1. Count the number of individuals in the population
2. Quadraring is used to sample an area and count the number of individuals in that area
3.This is repeated a number of times to gain an estimate of the population size
(quadrating is a method of sampling different locations to compare them)
4.1 Ecosystems
-An ecosystem is a community of organisms in a particular habitat
-The community is made up of different population of different species interacting within that habitat.
Species = A group of organisms reproducing to give fertile offspring
Habitat (abiotic factors):
-Cycle of daylight
-Temperature
-Rainfall
-Humidity
-slope
(All are non-biological)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)